DBCO-NHS ester
| Cat. # | Quantity | Price | Lead time | Buy this product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34720 | 10 mg | $80 | in stock | |
| 44720 | 25 mg | $110 | in stock | |
| 54720 | 50 mg | $135 | in stock | |
| 64720 | 100 mg |
$210
|
in stock | |
| 94720 | 1 g |
$1000
|
in stock | |
| K4720 | 5 g |
$3570
|
in stock |

Dibenzocyclooctyne (ADIBO, DBCO) is one of the most reactive cycloalkynes for strain-promoted alkyne azide cycloaddition (SPAAC) — a copper-free click chemistry reaction.
DBCO reacts instantly with azides. The reaction rate is much higher than that of copper-catalyzed reaction, and reactions with many other cyclooctynes. Unlike some other cyclooctynes, DBCO does not react with tetrazines — this allows to carry out orthogonal conjugation of azides with DBCO, and trans-cyclooctenes with tetrazines.
This amine-reactive NHS ester provides easy attachment of the reactive moiety to almost any primary or secondary amine group, such as protein, peptide, or small molecule amine.
Recommended protocol
Calculator
Customers also purchased with this product
Alkyne maleimide
Maleimide reagent for the attachment of alkyne functional group to proteins, peptides, and other molecules bearing SH (thiol) groups, including cysteine residues.6-Carboxy-H2DCFDA (6-carboxy-2',7'-dichlorodihydrofluorescein)
A reagent for detecting reactive oxygen species (ROS) in living cells. This carboxylated H2DCFDA analog has two additional negative charges that impede its leakage out of the cell.BDP® FL amine
Amino derivative of BDP FL dye, borondipyrromethene dye for FAM (fluorescein) 488 nm channel.General properties
| Appearance: | off white solid |
| Mass spec M+ increment: | 315.1 |
| Molecular weight: | 430.45 |
| CAS number: | 1384870-47-6 |
| Molecular formula: | C25H22N2O5 |
| IUPAC name: | 6-{2-Azatricyclo[10.4.0.04,9]hexadeca-1(16),4,6,8,12,14-hexaen-10-yn-2-yl}-6-oxohexanamide |
| Solubility: | good in DCM, DMF, DMSO |
| Quality control: | NMR 1H, HPLC-MS (95%) |
| Storage conditions: | Storage: 12 months after receival at -20°C in the dark. Transportation: at room temperature for up to 3 weeks. Avoid prolonged exposure to light. Desiccate. |
| MSDS: | Download |
| Product specifications |
Product citations
- Mitchell, M.I.; Ben‐Dov, I.Z.; Ye, K.; Liu, C.; Shi, M.; Sadoughi, A.; Shah, C.; Siddiqui, T.; Okorozo, A.; Gutierrez, M.; Unawane, R.; Biamonte, L.; Parihk, K.; Spivack, S.; Loudig, O. Exhaled breath condensate contains extracellular vesicles (EVs) that carry miRNA cargos of lung tissue origin that can be selectively purified and analyzed. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 2024, 13(4), e12440. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12440
- Mitchell, M.I.; Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, T.; Hazan, R.B.; Bauer, T.L.; Zakrzewski, J.; Donnelly, K.; Chow, K.; Ma, J.; Loudig, O. Non-invasive detection of orthotopic human lung tumors by microRNA expression profiling of mouse exhaled breath condensates and exhaled extracellular vesicles. Extracellular Vesicles and Circulating Nucleic Acids, 2024, 5(1), 138-64. doi: 10.20517/evcna.2023.77
- Mitchell, M.I.; Khalil, M.; Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Alverez-Perez, J.; Illsley, N.P.; Zamudio, S.; Al-Khan, A.; Loudig, O. Customizing EV-CATCHER to Purify Placental Extracellular Vesicles from Maternal Plasma to Detect Placental Pathologies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024, 25(10), 5102. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105102
- Gabold, B.; Adams, F.; Brameyer, S.; Jung, K.; Ried, C. L.; Merdan, T.; Merkel, O. M. Transferrin-Modified Chitosan Nanoparticles for Targeted Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Proteins. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res., 2023, 13(3), 822–838. doi: 10.1007/s13346-022-01245-z





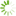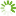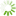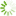






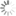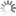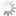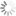
 $
$ 
